Ціна помилки чи дефекту
Перш ніж почати розгляд тестів. Варто зазначити кілька моментів, які можуть допомогти у виявленні правильної відповіді на тест.

Чим раніше буде знайдено помилку, тим менші наслідки це матиме для проєкту і тим легше таку помилку буде виправити.
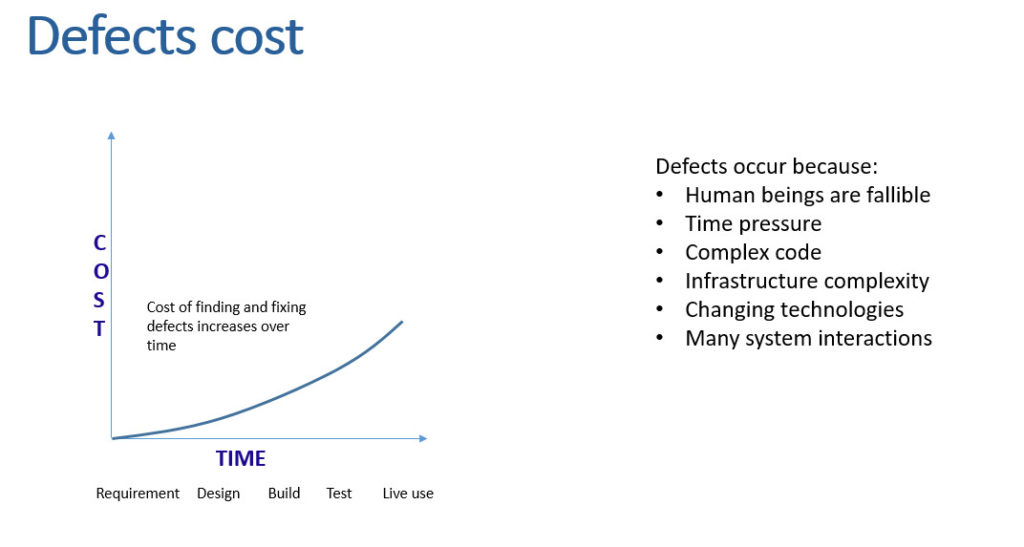
І ще один момент. Чим раніше виявляється помилка чи дефект, тим дешевше їх виправити.
Якість ПЗ
Якість ПЗ – ступінь, в якій система, компонент або процес задовольняють потреби або очікування замовника або користувача.
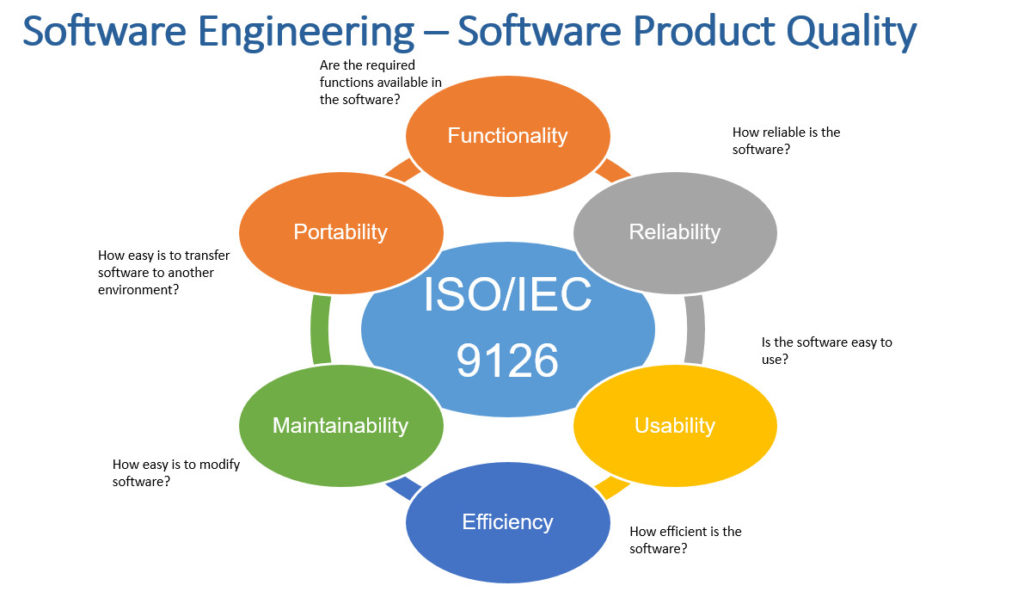
Функціональність (Functionality) – визначається здатністю ПЗ вирішувати завдання, які відповідають зафіксованим і очікуваним потребам користувача, за заданих умов використання ПЗ. Тобто ця характеристика відповідає за те, що ПЗ працює справно і точно, функціонально сумісно, відповідає стандартам галузі та захищене від несанкціонованого доступу.
Надійність (Reliability) – здатність ПЗ виконувати необхідні завдання у зазначених умовах протягом заданого проміжку часу або вказаної кількості операцій. Атрибути даної характеристики – це завершеність і цілісність всієї системи, здатність самостійно і коректно відновлюватися після збоїв у роботі, відмовостійкість.
Зручність використання (Usability) – можливість легкого розуміння, вивчення, використання і привабливість ПЗ для користувача.
Ефективність (Efficiency) – здатність ПЗ забезпечувати необхідний рівень продуктивності згідно з виділеними ресурсами, часом та іншими зазначеними умовами.
Зручність супроводу (Maintainability) – легкість, з якою ПЗ може аналізуватися, тестуватися, змінюватися для виправлення дефектів, для реалізації нових вимог, для полегшення подальшого обслуговування та адаптуватися до наявного оточення.
Портативність (Portability) – характеризує ПЗ з точки зору легкості його перенесення з одного оточення (software/hardware) в інше.
Варто зазначити, що зараз є і діє серія стандартів ISO 25000, в якій міститься новий підхід до якості. Зокрема збільшення характеристик і виділення “підрівнів” чи додаткових характеристик якості. Тим не менше цей підхід вважається трохи ускладненим, тому для початківців часто дають саме попередню версію ISO 9126. Яка простіша для розуміння і вивчення якої полегшить процес ознайомлення з новою концепцією серії стандартів 25000.
Розбір тестових питань по першому розділу
В цьому відео робиться спроба розібрати кілька десятків питань по першому розділу сілабусу ISTQB CTFL.
Всі питання з відео з правильними відповідями наводяться нижче.
Question 1
Which of the following is most important to promote and maintain good relationships between testers and developers?
- Understanding what managers value about testing.
- Explaining test results in a neutral fashion.
- Identifying potential customer work-arounds for bugs.
- Promoting better quality software at any cost.
Question 2
Which is not a testing principle
- Early testing.
- Pesticide paradox.
- Exhaustive testing.
- Defect clustering.
Question 3
According to the ISTQB Glossary, a risk relates to which of the following?
- Negative consequences that could occur.
- Negative consequences that will occur.
- Negative feedback to the tester.
- Negative consequences for the test object.
Question 4
According to the ISTQB Glossary, the word ‘bug’ is synonymous with which of the following words?
- Defect
- Mistake
- Error
- Incident
Question 5
A test team consistently find between 90% and 95% of the defects present in the system under test. While the test manager understands that this is a good defect-detection percentage for her test team and industry, senior management and executives remain disappointed in the test group, saying that the test team misses too many bugs. Given that the users are generally happy with the system and that the failures which have occurred have generally been low impact, which of the following testing principles is most likely to help the test manager explain to these managers and executives why some defects are likely to be missed?
- Absence-of-errors fallacy
- Exhaustive testing is impossible
- Defect clustering
- Pesticide paradox
Question 6
Deciding How much testing is enough should take into account: (i). Level of Risk including Technical and Business product and project risk. (ii.) Project constraints such as time and budget. (iii.) Size of Testing Team. (iv.) Size of the Development Team.
- i,ii,iv are true and ii is false.
- i,ii,iii are true and iv is false.
- i,ii are true and iii,iv are false.
- ii,iii,iv are true and i is false.
Question 7
Typically, exit criteria may consist of:
- Defining the amount, level of detail structure, and templates for the test documentation.
- Estimates of defect density or reliability measures.
- Adequacy of the test approaches taken.
- Discussions on disaster recovery.
Question 8
Detecting a defect at which of the following stage is most economical?
- Build.
- Deployment.
- Testing.
- Design.
Question 9
During which test activity could faults be found most cost effecftively?
- Execution.
- Design.
- Check Exit criteria completion.
- Planning.
Question 10
Ensuring that test design starts during the requirements definition phase is important to enable which of the following test objectives?
- Finding defects through dynamic testing.
- Preventing defects in the system.
- Finishing the project on time.
- Gaining confidence in the system.
Question 11
What factors should be considered to determine whether enough testing has been performed? I. The exit criteria. II. The budget. III. How big the test team is. IV. The product’s risk profile. V. How good the testing tools are. VI. Sufficient details of the system status to allow decisions
- i and ii and iv and vi
- i and ii and iii and vi
- ii and iii and iv and v
- i and ii and v and vi
Question 12
Evaluating testability of the requirements and system are a part of which phase?
- Test Implementation and execution.
- Test Analysis and Design.
- Evaluating exit criteria and reporting.
- Test Planning and control.
Question 13
Test Implementation and execution has which of the following major tasks? I. Developing and prioritizing test cases, creating test data, writing test procedures and optionally preparing the test harnesses and writing automated test scripts. II. Creating the test suite from the test cases for efficient test execution. III. Verifying that the test environment has been set up correctly. IV. Determining the exit criteria.
- I,II are true and III, IV are false
- I,IV,III are true and II is false
- II,III,IV are true and I is false
- I,II,III are true and IV is false
Question 14
Test planning has which of the following major tasks? I. Determining the scope and risks, and identifying the objectives of testing. II. Determining the test approach (techniques, test items, coverage, identifying and interfacing the teams involved in testing, testware). III. Reviewing the Test Basis (such as requirements, architecture, design, interface) IV. Determining the exit criteria.
- I,III,IV are true and II is false.
- I,II,IV are true and III is false.
- I,II are true and III,IV are false.
- II,III,IV are true and I is false.
Question 15
Which of the following are ‘Exit Criteria’?
- Acceptance criteria, completion criteria, pass/fail criteria.
- Coverage of code, schedule, estimates of defect density.
- The last executable statement within a component.
- Cost overruns.
Question 16
Testing Process comprised of
- Test Plan and Test Cases.
- Test Log and Test Status.
- Defect Tracking.
- All of the above.
Question 17
Which of the following are valid test objectives? I. Finding defects. II. Gaining confidence about the level of quality and providing information. III. Preventing defects. IV. Debugging the code.
- i, ii and iii
- i, ii and iv
- ii and iii
- i and iv
Question 18
The goal of software testing is to
- Validate that the system behaves as expected.
- Let the developer know the defects injected by him.
- Execute the program with the intent of finding errors.
- Debug the system.
Question 19
Though activities in the Fundamental test process may overlap or occur concurrently, identify the logical sequential process. (i) Test Implementation and Execution (ii) Test Closure activities (iii) Evaluating exit criteria and reporting (iv) Test Planning and Control (v) Test Analysis and Design
- v – i – iii – ii – iv
- iv – v – iii – ii – i
- iv – v – i – iii – ii
- v – ii – iii – i – iv
Question 20
What is not the primary data given by the tester in test execution?
- Number of test executed to date.
- Number of test cases written for change request.
- Total number of tests.
- Number of tests executed successfully to date.
Question 21
What is the need for test planning?
- to understand testing process.
- to perform ad hoc testing.
- to utilize a balance of testing techniques.
- to collect metrics.
Question 22
Which of the following test organizations has the highest level of independence?
- Independent testers within the development teams
- Independent testers from the user community
- Independent test specialists for specific test types, such as usability, performance or certification test specialists
- Code tested by another developer from the development team
Question 23
What is the USUAL sequence for performing the following activities during the Fundamental Test Process? (a) Analyze the test basis documents. (b) Define the expected results. (c) Create the test execution schedule. (d) Establish the traceability of the test conditions
- d, a, c, b
- a, d, c
- a, d, b, c
- a, b, c, d
Question 24
What should be taken into account to determine when to stop testing? I Technical risk; II Business risk; III Project constraints; IV Product documentation
- I, II, and IV are true; III is false
- I and II are true. III and IV are false
- I, II, and III are true, IV is false.
- III is true, I, II, and IV are false
Question 25
When should you stop testing?
- when the test completion criteria have been met.
- when no faults have been found by the tests run.
- when all planned tests have been run.
- when time for testing has run out.
Question 26
When what is visible to end-users is an imperfection in a work product where it does not meet its requirements, this is called:
- An error.
- A defect.
- A fault.
- A mistake.
Question 27
Which activities form part of test planning? (i) Developing test cases. (ii) Defining the overall approach to testing. (iii) Assigning resources. (iv) Building the test environment. (v) Writing test conditions.
- iv& v are true, i, ii & iii are false.
- i, ii &iv are true, iii & v are false.
- i, ii & iii are true iv& v are false.
- ii & iii are true, i, iv& v are false.
Question 28
It is recommended to perform exhaustive tests for covering all combinations of inputs and preconditions
- Yes, it’s strongly recommended.
- No, risk analysis and priorities should be used to focus testing efforts
- Yes, and it’s also necessary to include all the exit combinations
- Only the expert testers can make exhaustive tests.
Question 29
Which of the following is a major task of test planning?
- Preparing test specifications.
- Evaluating exit criteria and reporting.
- Determining the test approach.
- Measuring and analyzing results.