Рівні незалежності
- Жодних незалежних тестувальників
- Незалежні тестувальники в групах розробників
- Незалежна тестова група або група в організації
- Незалежні тестувальники від бізнес-організації або спільноти користувачів
- Незалежні спеціалісти з тестування для певних типів тестів: тестувальники юзабіліті, тестувальники безпеки тощо.
- Незалежні тестувальники, надані аутсорсингом або зовнішні для організації
Завдання тестового менеджера
- Планування тестування, обрання інструментів, підходів до тестування, оцінка часу, зусиль та вартості тестування, придбання, ресурсів, визначення рівнів тестування, циклів та планування управління інцидентами, вирішення, чи потрібна автоматизація
- Вирішення, які тестові середовища потрібні
- Представлення та аналіз показників моніторингу
- Адаптація планування на основі моніторингу
- Підготовка підсумкових звітів про тестування
Завдання тестувальника
- Створення специфікації тесту та перегляд тестів
- Використання інструментів адміністрування та керування тестами, а також інструментів моніторингу тестів
- Підготувка та отримання тестових даних
- Впровадження тестів на всіх рівнях тестування
- Виконання, автоматизація тестів
- Перегляд планів тестування та внесення свго внеску у них
Тестове планування
Структура документа з планування тестування охоплюється «Стандартом документації тестування програмного забезпечення» (IEEE 829, попередня але все ще багато в чому актуальна версія):
- Політика тестування (організація)
- Стратегія тестування (продукт)
- Генеральний план тестування (проєкт)
- План перевірки рівня (деталі)
Завдання тестового планування
- Підхід до тестування та процедури тестування, включаючи визначення рівнів тестування та критеріїв входу та виходу
- Ризики та цілі тестування
- Що тестувати, які ролі виконуватимуть тестову діяльність, які потрібні ресурси та хто їх використовуватиме
- Як повинні проводитися тестові дії, як будуть оцінюватися результати тестування
- Метрики для моніторингу та контролю підготовки та виконання тестів, усунення дефектів і проблем із ризиками
- Планування аналізу та проєктування тестів, впровадження, виконання та оцінювання тестів
- Тестова документація: обсяг, рівень деталізації, структура та шаблони
- Інтеграція та координація діяльності з тестування в діяльність життєвого циклу програмного забезпечення
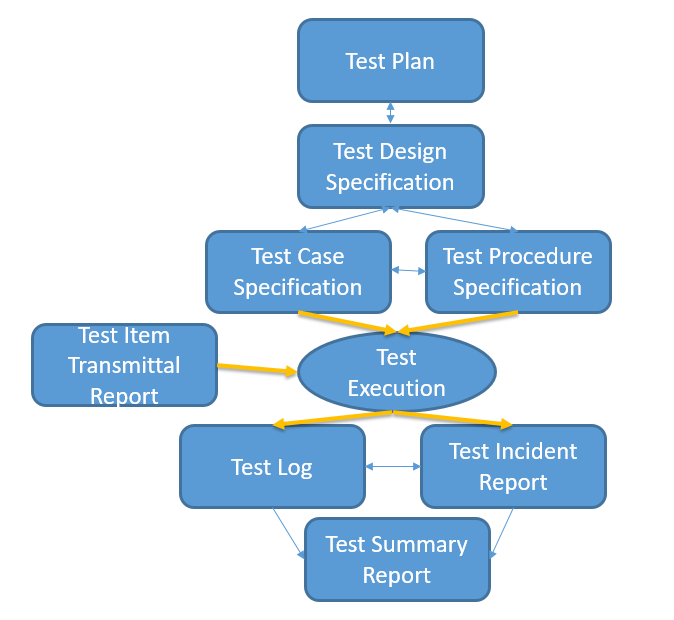
План тестування
План тестування містить наступні елементи:
- Ідентифікатор плану тестування
- Список літератури
- Вступ
- Тестові елементи
- Ризики програмного забезпечення
- Функції для перевірки
- Функції, які не підлягають тестуванню
- Підхід
- Критерії проходження/непроходження предмета
- Критерії призупинення/відновлення
- Результати тестування
- Тестові завдання, що залишилися
- Потреби середовища
- Потреби в кадрах і навчанні
- Обов’язки
- Розклад
- Планування ризиків і непередбачених ситуацій
- Дозволи
- Глосарій
Критерії входу/виходу
| Entry Criteria | Exit Criteria |
| Наявність та готовність тестового середовища | Метрики ретельності, такі як покриття коду, функціональність або ризик |
| Готовність тестових інструментів у тестовому середовищі | Оцінка щільності дефектів або метриків надійності |
| Наявність коду, який можливо тестувати | Варість |
| Наявність тестових даних | Графіки такі як ті, що базуються на часі до виходу на ринок |
| Залишкові ризики, такі як невиправлені дефекти або нестача тестового покриття в певних областях |
Тестова оцінка
- Підхід на основі показників або підхід на основі експертної думки
- Характеристики продукту: тестова база, розмір продукту, складність предметної області, вимоги
- Характеристики процесу розробки: стабільність організації, інструменти, що використовуються, процес тестування, навички залучених людей і тиск часу
- Результат тестування: кількість дефектів і обсяг необхідних доопрацювань
Тестові процеси моніторингу та контролю
- Щільність дефектів – кількість дефектів, виявлених у компоненті чи системі, поділена на розмір компонента чи системи (виражений у стандартних термінах вимірювання, наприклад, рядків коду, кількість класів або функціональних точок)
- Частота збоїв – кількість збоїв за одиницю часу, кількість збоїв у кількості транзакцій, кількість збоїв у кількості запусків комп’ютера.
Моніторинг прогресу тестування
- Забезпечте зворотній зв’язок і наочність щодо тестової діяльності
- Метрики використовуються для оцінки прогресу
- Відсоток виконаної роботи при підготовці тесту
- Відсоток виконаної роботи з підготовки тестового середовища
- Інформація про дефекти
- Тестове покриття вимог, ризиків або коду
- Суб’єктивна довіра тестувальників до продукту
- Дати тестових контрольних точок
- Витрати на тестування, включаючи вартість майбутніх знайдених помилок
Тестова звітність
- Опис підсумкового звіту про тестування наведено в «Стандарті документації тестування програмного забезпечення» (IEEE 829).
- Узагальнення інформації про тестування
- Що сталося під час тестування
- Проаналізована інформація та досягнуті показники
- Досягнуті результати: адекватність цілей тесту для цього рівня тесту, адекватність використаних тестових підходів, ефективність тестування щодо поставлених цілей.
Тестовий контроль
Тестовий контроль описує будь-які керівні чи коригувальні дії під час тестового циклу:
- Прийняття рішень на основі інформації тестового моніторингу
- Зміна пріоритетів тестів
- Зміна розкладу тестування через наявність або відсутність тестового середовища
- Зміна критерію вступу
Управління конфігураціями
Встановити та підтримувати цілісність продуктів. Все має бути пов’язано. Керування конфігурацією допомагає:
- Унікально ідентифікувати (і відтворити) тестований елемент, тестові документи, тести та тестові джгути
- Контролювати зміни цих характеристик
- Записувати та повідомляти про зміни
- Статус обробки та реалізації
- Перевірка відповідності встановленим вимогам
Ризик і тестування
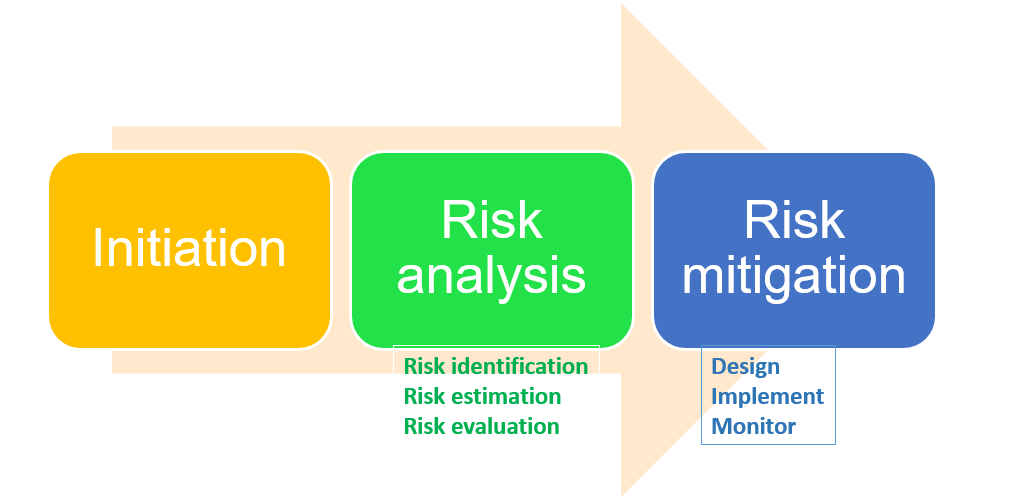
Ризик можна визначити як можливість того, що подія станеться та призведе до потенційної проблеми. Рівень ризику визначатиметься ймовірністю та впливом.
Проєктні Ризики
Проєктні ризики – це ризики, пов’язані зі здатністю проєкту досягати своїх цілей.
Потенційні області збою в програмному забезпеченні або системі відомі як ризики продукту.
| Проектні ризики | Продуктові ризики |
| Організаційні фактори (люди та навички) | Поставлено схильне до збоїв ПЗ |
| Технічні проблеми (вимоги, середовище, код) | Імовірність того, що програмне/апаратне забезпечення може завдати шкоди особі чи компанії |
| Питання постачальника | Низькі характеристики програмного забезпечення (наприклад, функціональність, надійність, зручність використання та продуктивність) і цілісність даних |
| Договірні питання | Програмне забезпечення, яке не виконує своїх призначених функцій |
Підхід заснований на ризику
Створіть проактивні можливості для зниження рівня ризику продукту, починаючи з початкових етапів проекту:
- Визначте методи тестування, які необхідно використовувати
- Визначте обсяг тестування, яке необхідно провести
- Надайте пріоритет тестуванню, щоб якомога раніше виявити критичні дефекти
- Визначте, чи можна використовувати будь-яку діяльність, не пов’язану з тестуванням, для зменшення ризику (наприклад, навчання недосвідчених спеціалістів)
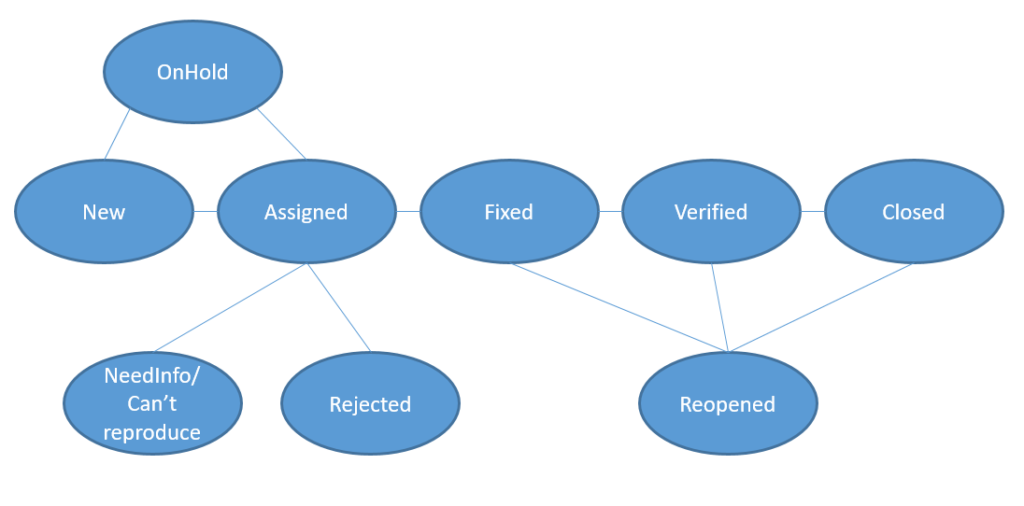
Управління дефектами (статуси)
Розбір тестових питань по п’ятому розділу
В цьому відео робиться спроба розібрати кілька десятків питань по п’ятому розділу сілабусу ISTQB CTFL.
Всі питання з відео з правильними відповідями наводяться нижче.
Question 1
Which of the following metrics would be most useful to monitor during test execution?
- Percentage of requirements for which a test has been written.
- Number of defects found and fixed.
- Number of test environments remaining to be configured.
- Percentage of test cases written.
Question 2
Which of the following is most likely to be mentioned as a project risk?
- Unexpected illness of a key team member
- Data corruption under network congestion
- Failure to handle a key use case
- Excessively slow transaction-processing time
Question 3
A test engineer is testing a Video Player (VCR), and logs the following report:
Title: Fast Forward stops after 2 minutes. It happens every time
Expected result: Fast forward continues till the end of the tape
Severity: High
Priority: Urgent
What important information did the engineer leave out?
- Ideas for the test case improvement
- History of the report
- Actual result
- Identification (Software and hardware) of the VCR
Question 4
Which of the following risks represents the highest level of risk to the project:
- Likelihood of failure = 1%, potential cost of impact = $1 m.
- Likelihood of failure = 10%, potential cost of impact = $500,000.
- Likelihood of failure = 20%, potential cost of impact = $150,000.
- Likelihood of failure = 5%, potential cost of impact = $500,000.
Question 5
A product risk analysis meeting is held during the project planning period. Which of the following determines the level of risk?
- The price for which the software is sold
- Difficulty of fixing related problems in code
- The technical staff in the meeting
- The harm that might result to the user
Question 6
Which of the following statements is most true about test conditions?
- An item or event of a component or system that can be verified by one or more test cases.
- The grouping of a composite set of test cases which, when tested as a whole, reveal a positive or negative result.
- A testable component derived from business requirements.
- Applies to software testing only.
Question 7
A Test Plan Outline contains which of the following: (i.) Test Items (ii.) Test Scripts (iii.) Test Deliverables (iv.) Responsibilities
- i,ii are false and iii , iv are true
- i,iii,iv are true and ii is false
- i,ii,iii are true and iv is false
- ii,iii are true and i and iv are false
Question 8
According to the ISTQB Glossary, a product risk is related to which of the following?
- A single test item
- The test object
- Control of the test project
- A potential negative outcome
Question 9
According to the ISTQB Glossary, what do we call a document that describes any event that occurred during testing which requires further investigation?
- An incident report
- A test summary report
- A bug report
- A defect report
Question 10
According to the ISTQB Glossary, what do we mean when we call someone a test manager?
- A test manager manages a collection of test leaders.
- A test manager gets paid more than a test leader.
- A test manager is the leader of a test team or teams.
- A test manager reports to a test leader.
Question 11
According to the ISTQB Glossary, what is a test level?
- An ISTQB certification.
- A test type.
- A group of test activities that are organized together.
- One or more test design specification documents.
Question 12
Based on the IEEE Standard for Software Test Documentation (IEEE Std 829), which of the following sections are part of the test summary report?
(a.) Summary
(b.) Test incident report identifier
(c.) Test deliverables
(d.) Risks and contingencies
(e.) Variances
(f.) Approvals
(g.) Output specifications
- a, c and d
- a, b and f
- a, d and e
- a, e and f
Question 13
During test execution, the test manager describes the following situation to the project team:
‘90% of the test cases have been run.
20% of the test cases have identified defects.
127 defects have been found.
112 defects have been fixed and have passed confirmation testing.
Of the remaining 15 defects, project management has decided that they do not need to be fixed prior to release.’
Which of the following is the most reasonable interpretation of this test status report?
- The remaining 15 defects should be confirmation tested prior to release.
- The programmers should focus their attention on fixing the remaining known defects prior to release.
- The remaining 10% of test cases should be run prior to release.
- The system is now ready for release with no further testing or development effort.
Question 14
Given the following sets of test management terms (v-z), and activity description (1-5), which one of the following best pairs the two sets?
v – Test control.
w – Test monitoring.
x – Test estimation.
y – Incident management.
z – Configuration control.
1 – Calculation of required test resources.
2 – Maintenance of record of test results.
3- Re-allocation of resources when tests overrun.
4 – Report on deviation from test plan.
5 – Tracking of anomalous test results.
- v-3, w-4, x-1, y-5, z-2
- v-2, w-5, x-1, y-4, z-3
- v-3, w-2, x-1, y-5, z-4
- v-2, w-1, x-4, y-3, z-5
Question 15
From a Testing perspective, what are the MAIN purposes of Configuration Management?:
(i) Identifying the version of software under test.
(ii) Controlling the version of testware items.
(iii) Developing new testware items.
(iv) Tracking changes to test ware items.
(v) Analysing the need for new testware items.
- i, ii and iv.
- i, iii and v.
- ii, iii and iv,
- ii, iv and v.
Question 16
In a risk-based approach the risks identified may be used to :
(i.) Determine the test technique to be employed
(ii.) Determine the extent of testing to be carried out
(iii.) Prioritize testing in an attempt to find critical defects as early as possible.
(iv.) Determine the cost of the project
- ii is True; i, iii, iv are False
- i,ii,iii are true and iv is false
- ii & iii are True; i, iv are False
- ii, iii & iv are True; i is false
Question 17
In an incident report, the tester makes the following statement, At this point, I expect to receive an error message explaining the rejection of this invalid input and asking me to enter a valid input. Instead the system accepts the input, displays an hourglass for between one and five seconds and finally terminates abnormally, giving the message, “Unexpected data type: 15.Click to continue.” ‘ This statement is likely to be found in which of the following sections of an IEEE 829 standard incident report?
- Item pass/fail criteria
- Summary
- Impact
- Incident description
Question 18
Metrics collected during testing includes
- System test cases planned / executed / passed.
- Discrepancies reported / resolved.
- Staff hours.
- All of the above.
Question 19
Poor software characteristics are
- Only Project risks
- Only Product risks
- Project risks and Product risks
- Project risks or Product risks
Question 20
The following best describes the defect density:
- Ratio of discovered errors per size of code.
- Number of modifications made per size of code.
- Number of failures reported against the code.
- Ratio of failure reports received per unit of time.
Question 21
Which of the following processes ensures that all items of testware are identified, version controlled, tracked for changes, so that traceability can be maintained throughout the test process?
- Software traceability process
- Incidence management process
- Testing design process
- Configuration management process
Question 22
The ISTQB Foundation Syllabus establishes a fundamental test process where test planning occurs early in the project, while test execution occurs at the end. Which of the following elements of the test plan, while specified during test planning, is assessed during test execution?
- Test tasks
- Test team training
- Exit criteria
- Environmental needs
Question 23
What is the KEY difference between preventative and reactive approaches to testing?
- Preventative testing is always analytical; reactive testing is always heuristic.
- Preventative tests are designed after the software has been produced; reactive tests are designed early in response to review comments.
- Preventative tests and reactive tests are designed as early as possible.
- Preventative tests are designed early; reactive tests are designed after the software has been produced.
Question 24
What is the primary difference between the test plan, the test design specification, and the test procedure specification?
- The test plan is for managers, the test design specification is for programmers and the test procedure specification is for testers who are automating tests.
- The test plan is the least thorough, the test procedure specification is the most thorough and the test design specification is midway between the two.
- The test plan describes one or more levels of testing, the test design specification identifies the associated high-level test cases and a test procedure specification describes the actions for executing a test.
- The test plan is finished in the first third of the project, the test design specification is finished in the middle third of the project and the test procedure specification is finished in the last third of the project.
Question 25
What needs to be done when there is an insufficient time for testing
1. Do Ad-hoc testing.
2. Do usability testing.
3. Do sanity testing.
4. Do a risk based analysis to prioritize.
- 1 and 2.
- 3 & 4.
- All of the above.
- None of the above.
Question 26
What is Risk analysis?
- Evaluating risks.
- Evaluating controls.
- Evaluating vulnerabilities.
- All of the above.
Question 27
Which factors contribute to humans making mistakes that can lead to faulty software?
(I.) Setting aggressive schedule
(II.) Integrating complex systems
(III.) Allocating adequate resources
(IV.) Failing to control changes
- I, II and IV are true; III is false
- II and IV are true; I and III are false
- I, II and III are true; IV is false
- I and II are true; III and IV are false
Question 28
What content would be in an incident report if that incident report was based on the IEEE 829 Standard for Software Test Documentation?
(i). Identification of configuration items of the software or system.
(ii). Software or system lifecycle process in which the incident was observed.
(iii). Description of the anomaly to enable reproduction of the incident.
(iv). Number of occurrences of the incident.
(v). Classification of the cause of the incident for metrics and for reporting purposes.
- i, ii, iii
- ii, iii
- i, iii, iv
- i, ii, iii, v
Question 29
Why is independent testing important?
- Independent testing is more effective at finding defects.
- Independent testers should determine the processes and methodologies used.
- Independent testers are dispassionate about whether the project succeeds or fails.
- Independent testing is usually cheaper than testing your own work.
Question 30
Which of the following is among the typical tasks of a test leader?
- Keep tests and test coverage hidden from programmers.
- Develop system requirements, design specifications and usage models.
- Handle all test automation duties.
- Gather and report test progress metrics.
Question 31
Which of the following factors is an influence on the test effort involved in most projects?
- The departure of the test manager during the project.
- Unexpected long-term illness by a member of the project team.
- The quality of the information used to develop the tests.
- Geographical separation of tester and programmers.